What is an Employer of Record (EOR)?
January 30th, 2025

Definition and Purpose of EOR
If you’ve ever wondered how businesses manage employees across the globe without setting up legal entities in every country, the answer often lies with an Employer of Record (EOR). This modern employment solution has become a game-changer in today’s global economy.
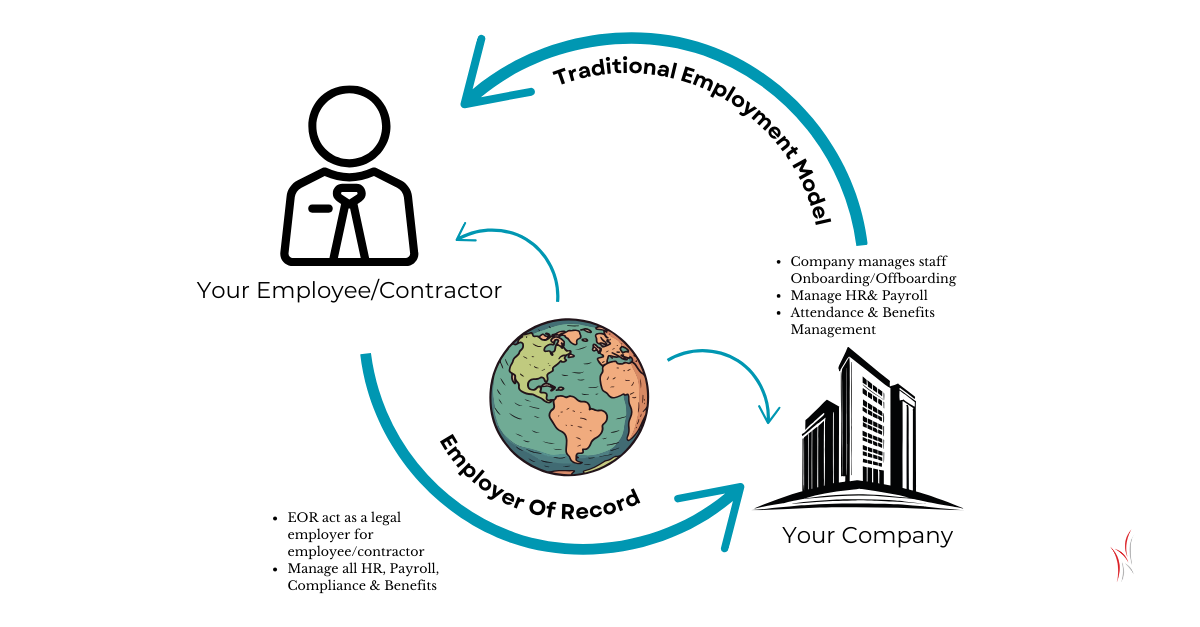
An Employer of Record (EOR) is a third-party organization that takes on the formal responsibility of employing workers on behalf of another company. Essentially, the EOR handles all employment-related tasks, such as payroll, tax compliance, and benefits administration, while the client company retains control over daily operations and management.

EOR vs. Traditional Employment Models
Unlike traditional employment models where a company directly employs its staff, an EOR legally employs the workers while the client company oversees their tasks. This distinction allows businesses to operate in regions where they lack a legal entity.
Businesses often use EOR services to simplify operations, particularly when expanding into new regions. By outsourcing legal and administrative tasks, companies can focus on core functions while avoiding the complexities of navigating unfamiliar labor laws.
Why Businesses Need EORs
Expanding into new markets can be a logistical and legal headache. EORs simplify this process by ensuring compliance with local labor laws, reducing administrative burdens, and enabling companies to focus on their core business activities.
In the ever-evolving global business environment, companies are continually looking for ways to streamline operations, reduce risks, and optimize their workforce. One essential strategy that has gained prominence is employing an Employer of Record (EOR). In this comprehensive article, we delve deep into why businesses need EORs, exploring their benefits and the immense value they bring to organizations of all sizes.
Who Can Benefit from an EOR?
Startups
For startups with limited resources, an EOR provides a cost-effective solution to hiring and managing employees.
SMEs
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) looking to expand globally can benefit immensely from EOR services. These organizations can avoid the hassle of establishing local entities, enabling them to allocate resources to growth initiatives.
Companies Expanding Internationally
Firms entering new markets can rely on EORs to ensure compliance and avoid the expense of setting up local entities.
Remote-First Organizations
With remote work becoming the norm, many companies are hiring talent from different countries. EORs simplify the process by handling cross-border employment logistics, ensuring compliance and smooth operations.
Services Covered by an Employer of Record (EOR) in India

1. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Ensuring adherence to Indian labor laws such as the Factories Act, Shops and Establishments Act, and Payment of Wages Act.
- Compliance with tax laws, including Income Tax (TDS) and Goods and Services Tax (GST) where applicable.
- Managing legal documentation, including employment contracts aligned with local requirements.
- Filing statutory reports with the Ministry of Labour and Employment or other relevant authorities.
2. Payroll Management
- Processing monthly payroll and calculating wages, bonuses, and overtime as per local regulations.
- Ensuring accurate Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) filings for employees.
- Managing contributions to statutory funds like Employee Provident Fund (EPF) and Employee State Insurance (ESI).
- Providing detailed salary slips to employees.
3. Taxation and Statutory Contributions
- Ensuring timely filing and payment of:
- EPF contributions.
- ESI contributions for eligible employees.
- Gratuity payments under the Payment of Gratuity Act.
- Professional Tax (PT).
- Labour Welfare Fund (LWF).
- Filing necessary returns with the Income Tax Department and other statutory bodies.
4. Employee Benefits Management
- Managing statutory benefits like health insurance under ESI and retirement benefits under EPF.
- Administration of paid leaves, maternity/paternity benefits, and gratuity as per Indian law.
- Providing additional benefits such as private health insurance, accident coverage, or wellness programs (if applicable).
5. Recruitment and Onboarding
- Assisting with hiring local talent, including background verification and reference checks.
- Drafting employment agreements compliant with Indian labor laws.
- Managing employee onboarding and orientation.
6. Termination and Offboarding
- Handling employee termination or resignation in compliance with Indian labor laws (e.g., required notice period, severance payments).
- Managing full and final settlements, including pending wages, bonuses, and gratuity.
- Providing necessary documents like experience certificates or relieving letters.
7. HR Administration
- Providing guidance and support for performance management and dispute resolution.
- Maintaining employee records and ensuring data privacy compliance under the Personal Data Protection Bill.
- Responding to employee queries about payroll, benefits, or other HR concerns.
8. Local Expertise and Support
- Offering insights into regional labor trends, salary benchmarks, and recruitment strategies.
- Providing real-time assistance with HR or legal matters related to employment in India.
Define the EOR Relationship with Employee and Employer (Client Company)
In the modern workplace, companies are adopting new and flexible employment structures to cater to global expansion, diverse talent pools, and operational efficiency. One of the most popular employment models in such contexts is the Employer of Record (EOR) relationship. This term might sound complex, but in reality, it provides valuable insight into how employment and labor laws are handled in a global business environment. In this article, we’ll break down what EOR means and how it impacts the relationship between the employee and employer.
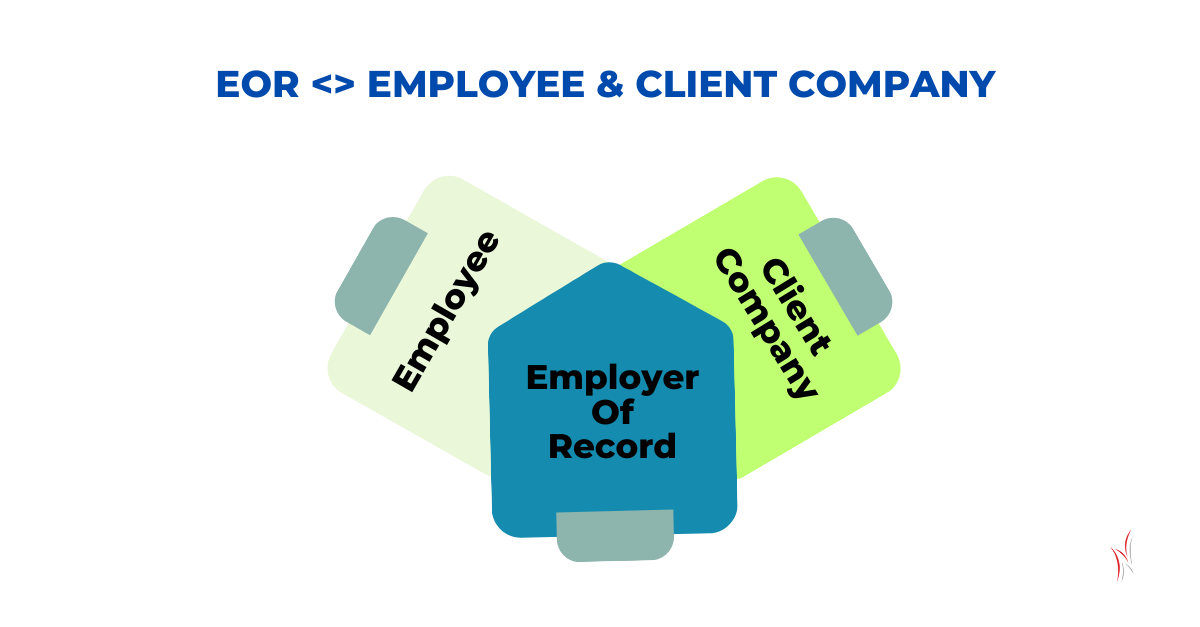
The Roles of the Employee and the Employer in an EOR Relationship
Understanding the roles of both parties—the employee and the employer—is critical to understanding the EOR framework.
Role of the Employee
From the employee’s perspective, their relationship with the EOR is similar to any other job, but with some important differences. While they still report to the client company and follow its guidelines and tasks, the legalities of employment, such as pay, benefits, and taxes, are handled by the EOR.
Key Responsibilities of the Employee:
- Performing the job as per the client company’s expectations.
- Communicating with both the client company and the EOR when necessary.
- Complying with the workplace rules set by the client company.
Role of the Employer (Client Company)
The client company, although not the official employer, manages the employee’s day-to-day work responsibilities. It defines the job tasks, sets the work culture, and expects outcomes, but the EOR manages all employment-related paperwork and legal obligations.
Key Responsibilities of the Client Company:
- Providing job-related guidance, tasks, and performance expectations.
- Managing the overall business objectives that require the employee’s expertise.
- Collaborating with the EOR to ensure compliance and smooth employee management.
Benefits of the EOR Relationship for Employees
The EOR model offers a number of benefits to employees, especially in international or remote work settings.
1. Access to Benefits and Protection
Since the EOR handles all legal employment requirements, employees are guaranteed the same protections and benefits as traditional employees, such as health insurance, paid time off, and retirement savings options.
2. Compliance with Local Labor Laws
For global companies, having an EOR ensures that employees are compliant with local labor laws. The EOR helps employees understand and navigate complex legal frameworks that may vary from country to country.
3. Reduced Legal Liabilities
With the EOR managing compliance, employees are shielded from potential legal issues related to employment rights, taxes, or international employment complications.
Key Responsibilities of the Client Company:
- Providing job-related guidance, tasks, and performance expectations.
- Managing the overall business objectives that require the employee’s expertise.
- Collaborating with the EOR to ensure compliance and smooth employee management.
Benefits of the EOR Relationship for Employers
The EOR relationship offers multiple benefits for employers, especially for businesses that are expanding into new territories or hiring a remote workforce.
1. Faster Global Expansion
Employers can expand quickly into new countries without the need to establish a legal entity in each jurisdiction. The EOR takes care of local labor laws, taxes, and compliance, allowing businesses to focus on growth and operations.
2. Simplified HR and Legal Processes
Managing payroll, benefits, and legal compliance for employees can be daunting. With an EOR, these tasks are outsourced to a specialized service, freeing up internal resources to focus on core business goals.
3. Risk Mitigation
Navigating local labor laws can be tricky, especially when managing a remote or international workforce. EORs provide a safety net, ensuring that businesses avoid potential legal risks, fines, and other issues related to mismanagement.
Benefits of Using an Employer of Record
Streamlined Global Hiring
Expanding into international markets can be daunting due to varying labor laws, tax regulations, and employment practices. EORs facilitate seamless global expansion by managing these complexities, allowing businesses to hire local talent without establishing a legal entity in the target country. This significantly reduces time-to-market and lowers operational costs.
Compliance with Local Laws
Navigating the intricate web of labor regulations in different jurisdictions is a challenge. EORs ensure compliance with local employment laws, including minimum wage requirements, employee rights, and termination protocols. This not only reduces the risk of legal penalties but also safeguards the company’s reputation.
Reduced Administrative Burden
Handling payroll, benefits administration, and tax filings can be resource-intensive. By outsourcing these tasks to an EOR, companies can focus on strategic initiatives rather than getting bogged down by administrative duties. This leads to improved efficiency and productivity.
Cost-Effectiveness
Setting up a local entity in a foreign market is not only time-consuming but also expensive. An EOR eliminates the need for such investments, offering a more affordable alternative for hiring and managing employees in multiple locations.
Access to Local Talent
EORs have an in-depth understanding of local job markets, enabling businesses to tap into a diverse talent pool. They streamline the hiring process by handling recruitment, onboarding, and employee management, ensuring businesses get the right talent for their needs.
How to Choose the Right EOR Provider
When selecting an EOR provider, it is crucial to consider the following factors:
Compliance with Local Laws
Navigating the intricate web of labor regulations in different jurisdictions is a challenge. EORs ensure compliance with local employment laws, including minimum wage requirements, employee rights, and termination protocols. This not only reduces the risk of legal penalties but also safeguards the company’s reputation.
- Global Coverage: Ensure the provider has expertise in the regions where you plan to expand.
- Compliance Expertise: Verify their track record in handling legal and regulatory requirements.
- Technology Integration: A good EOR provider should offer user-friendly platforms for payroll and employee management.
- Scalability: Choose a provider that can scale with your business needs.
- Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials to gauge their reliability and service quality.
Options of hiring international employees
In today’s globalized world, businesses are constantly expanding their reach, and hiring international employees has become an essential strategy for growth. But should you hire full-time employees or independent contractors? Both options come with distinct advantages and challenges that need to be considered. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between full-time employees and independent contractors, their benefits and challenges, and help you determine which option best suits your business needs.
How to Choose Between Full-Time Employees and Independent Contractors
Assessing Your Business Needs
Before making a decision, it’s important to assess the specific needs of your business. If you require long-term, dedicated employees, full-time hiring may be the best option. If you need short-term or specialized help, independent contractors may be more suitable.
Understanding Your Budget
Budget considerations play a major role in the decision-making process. Full-time employees typically incur more expenses due to salaries, benefits, and taxes, while independent contractors offer a more cost-effective option for temporary or project-based work.
Aligning with Company Goals
Consider your company’s long-term goals and how international hiring fits into your strategy. Full-time employees are more suited for companies seeking stable, consistent growth, while independent contractors are ideal for businesses that need flexibility and specialized expertise.
Here you can review the key classification of both role:
Full-Time Employees
Consider your company’s long-term goals and how international hiring fits into your strategy. Full-time employees are more suited for companies seeking stable, consistent growth, while independent contractors are ideal for businesses that need flexibility and specialized expertise.
Independent Contractors
Independent contractors, on the other hand, are self-employed individuals who work on a project basis. They are hired for specific tasks or assignments and have a greater degree of control over their work schedule and methods. Independent contractors do not receive the same benefits as full-time employees, and they are typically paid on a per-project or hourly basis.
Alternative of Employer of Record (EOR)
When expanding globally or managing remote teams, businesses face various challenges. One common solution businesses turn to is the Employer of Record (EOR) model. However, there are 3 relevant alternatives; PEO, Independent Contractor Model and Global Employment Solution to EORs (Local) that may better suit the unique needs of certain companies.
Why Consider Alternatives to Employer of Record?
This table provides a clear comparison of the key factors between EOR, Independent Contractor Model, Global Employment Solutions and PEO to help businesses choose the best option based on their needs.
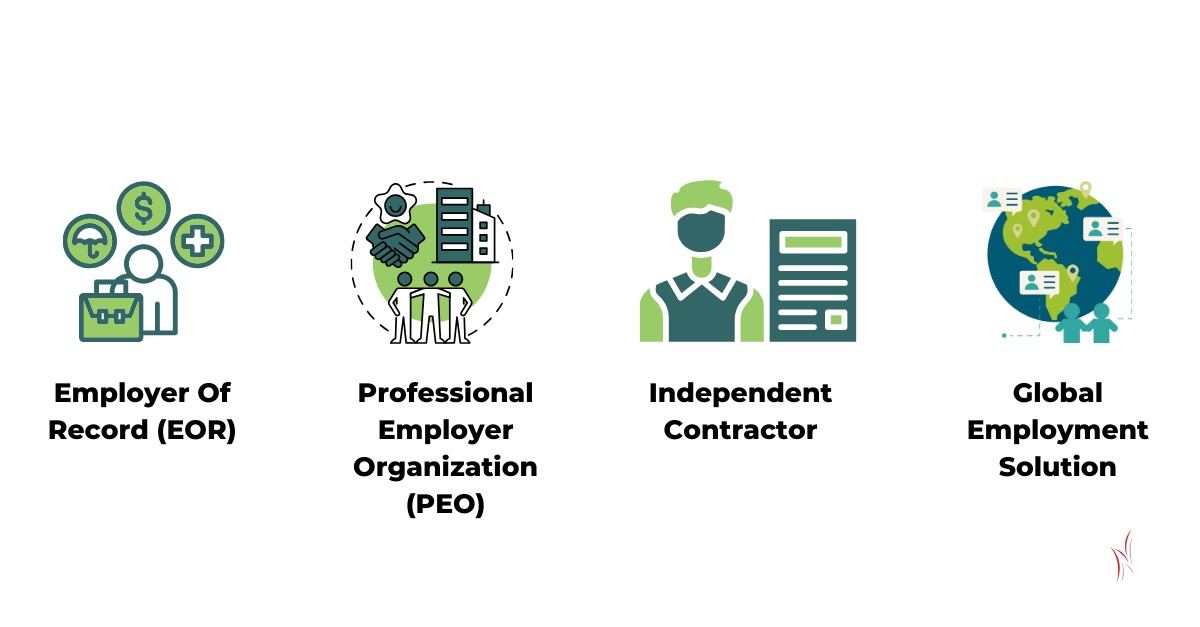

| Key Factors | EOR (Employer of Record) | Independent Contractor Model | Global Employment Solution | PEO (Professional Employer Organization) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Legal employer for hiring employees in a specific country or globally. | Engages individuals as independent contractors for short-term or project-based work. | Provides a solution for hiring globally, often focusing on contractors or mixed models. | Co-employer arrangement for domestic hiring and HR management. |
| Legal Compliance | Ensures full compliance with local labor laws, taxes, and employee protections. | High risk of worker misclassification; compliance burden on the company. | Varies based on the arrangement; compliance typically focused on contractors. | Provides compliance support but limited to domestic jurisdictions. |
| Employment Type | Full-time or part-time employees. | Independent contractors or freelancers. | Both employees and contractors depending on the structure. | Full-time employees only, within specific domestic regions. |
| Global Reach | Suitable for hiring employees globally. | Flexible for hiring globally, but lacks compliance frameworks. | Effective for global hiring, but more contractor-focused. | Limited to specific countries or regions; not ideal for global hires. |
| Benefits Management | Offers comprehensive benefits like health insurance, retirement, and leave. | No benefits provided; contractors manage their own. | Limited benefits for contractors; employees may receive some benefits. | Provides shared employee benefits within domestic markets. |
| Payroll Management | EOR handles payroll, taxes, and statutory filings for employees. | Company manages contractor payments; no payroll service included. | Handles payroll for employees or contractors globally. | Handles payroll for employees but within limited jurisdictions. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to full compliance and employee benefits. | Cost-effective as no statutory payments or benefits are required. | Varies based on scope; often mid-range. | Moderate cost; shared expenses for HR tasks. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; ideal for long-term employment relationships. | Highly flexible; best for short-term or project-based work. | Moderate flexibility for hybrid models of employees and contractors. | Less flexibility as it focuses on traditional employment. |
| Control Over Workforce | Company retains operational control; EOR manages legal and HR functions. | Company has full control over contractors but limited commitment. | Similar to EOR but less focused on long-term employment relationships. | Control shared between company and PEO for HR functions. |
| Risk Management | Minimizes risks of misclassification and compliance violations. | High risk of contractor misclassification leading to potential penalties. | Moderate risk; depends on proper worker classification and contracts. | Low risk for compliance within specific regions. |
| Scalability | Scalable for global employee hiring across multiple countries. | Scalable for hiring contractors but not employees globally. | Scalable for mixed workforce solutions globally. | Scalable for domestic hiring; limited for global expansion. |
| Onboarding & Offboarding | EOR handles onboarding, termination, and compliance tasks. | Company is responsible for managing these processes for contractors. | Often managed by the provider, similar to EOR. | Shared responsibility with PEO for these tasks. |
| Employee Engagement | Supports long-term relationships with employee benefits and protections. | Limited engagement as contractors work independently. | Engagement varies depending on the type of worker hired. | Focused on traditional employee engagement within domestic markets. |
| Administrative Burden | EOR takes full responsibility for HR, payroll, and compliance. | Company handles all administrative tasks for contractors. | Reduces administrative burden for global contractors/employees. | Shares administrative tasks with the company. |
| Best Use Case | For businesses expanding globally, hiring full-time employees in foreign markets. | For companies needing short-term, flexible work or project-based tasks. | For businesses managing global contractors or hybrid workforce models. | For domestic companies wanting to outsource HR and compliance tasks. |
What is Local EOR and Global EOR? Define Comparison and List Out Local EOR Pros Over Global EOR
Introduction
In the dynamic world of business, managing employees across different regions can be a logistical and legal challenge. This is where the Employer of Record (EOR) model steps in, simplifying workforce management. But what’s the difference between Local EOR and Global EOR, and how do they compare? Let’s dive in to find out.

Understanding Local EOR
Budget considerations play a major role in the decision-making process. Full-time employees typically incur more expenses due to salaries, benefits, and taxes, while independent contractors offer a more cost-effective option for temporary or project-based work.
Definition of Local EOR
A Local EOR is a service provider that takes on the responsibility of managing employment within a specific country. This includes handling payroll, taxes, compliance, and employee benefits for companies hiring in that country.
Key Functions of Local EOR
- Manages payroll and tax filings
- Offers localized HR support
- Handles employee contracts specific to the country
Examples of Local EOR in Practice
Imagine a company based in the U.S. hiring a team in Germany. A Local EOR would manage the German workforce, ensuring compliance with German labor laws without the U.S. company needing to set up a local entity.
Understanding Global EOR
Definition of Global EOR
A Global EOR operates on a larger scale, offering employment solutions across multiple countries. They act as the legal employer for international teams while ensuring compliance with each country’s labor laws.
Key Functions of Global EOR
- Manages compliance across multiple jurisdictions
- Provides standardized payroll services globally
- Offers a centralized HR system for international teams
Examples of Global EOR in Practice
For a multinational corporation hiring employees in multiple continents, a Global EOR would streamline operations, acting as the employer for all international hires.
Comparison Between Local EOR and Global EOR
Scope and Reach
- Local EOR: Operates within one specific country.
- Global EOR: Covers multiple countries, offering a broader reach.
Compliance and Legal Expertise
- Local EOR: Specializes in detailed, country-specific compliance.
- Global EOR: Manages overarching compliance while navigating the complexities of various jurisdictions.
Cost Implications
- Local EOR: Cost-effective for single-country operations.
- Global EOR: Higher costs due to broader services and scale.
Scalability
- Local EOR: Suitable for small-scale operations.
- Global EOR: Perfect for businesses planning rapid global expansion.
Flexibility in Operations
- Local EOR: Tailored solutions for country-specific needs.
- Global EOR: Standardized processes, ensuring consistency.
Pros of Local EOR Over Global EOR
In-depth Local Expertise
A Local EOR provides unmatched knowledge of regional laws and practices.
Cost-Effectiveness for Localized Operations
Hiring a Local EOR is more budget-friendly for companies focusing on one country.
Personalized and Tailored Solutions
Local EORs often offer more personalized services, catering to specific business needs.
Enhanced Relationship with Local Workforce
Being closer to the workforce allows Local EORs to establish better employee relationships.
Simplified Management
With a localized focus, management becomes less complex.
Challenges of Using Local EOR
- Restricted to one country, limiting scalability.
- Unsuitable for businesses seeking a global workforce.
Challenges of Using Global EOR
- Higher costs due to expansive operations.
- May lack granular expertise in specific regions.
When to Choose Local EOR vs. Global EOR
- Local EOR: Ideal for companies hiring in a single country with no immediate plans for expansion.
- Global EOR: Best for multinational corporations or those planning rapid international growth.
Local EORs and Global EORs serve different purposes. Your choice should align with your business goals, budget, and geographical needs. Both Local EOR and Global EOR have their advantages and limitations. If your focus is on localized operations, a Local EOR is your best bet. However, for businesses eyeing global expansion, a Global EOR offers unmatched scalability and consistency.
NSquareIT Offshore Agency: Your Local EOR partner in India
Our EOR services defined as below:
- Recruitment service: Screening, shortlisting candidate, submit the best suitable candidate to the client/employer to build their team.
- Core HR services: Employee onboarding, Employee Info & Document Management, Employee offboarding
- Payroll Management services: Payroll Input, Payroll Compliance, Payroll/Reimbursement/ Bonus Release, Payslip/Salary Slip release, TDS Calculation Management & Other administrative works
- Statutory Compliance Management service;
- Professional Tax (PT) & Provident Fund (PF) management: Monthly reports, remittances, UAN – Aadhar based linking, Filing of PF Nomination, Transfer and Withdrawals forms and obtaining acknowledgements, Filing monthly Online returns (for the applicable States)
- Leave Management: Leave policy implementation, Year end processing, Cloud based HRMS support and review by Manager, Leave Query and Resolution, Employee Addition/Deletion and Record Management.
NSquareIT Offshore Agency’s client onboarding process with simple and concise terms:
Our EOR services defined as below:
- Execute the MSA with NOA.
- Meet the Implementation team and get to know them.
- Complete a questionnaire to gather essential implementation details.
- Attend an Implementation meeting with the team where the following topics will be covered:
- Policy creation
- Compiling a list of holidays
- Recording of leave details
- Explanation of employment acts such as Maternity Act, Gratuity Act, etc.
- Collection of working hours, probation details, notice information, etc.
- Discussion of employment contracts and other policy documents
- Opportunity to ask questions and clarify doubts.
- Finalize all contracts and policies.
- Welcome your first employee aboard!
- Billing will begin once the first offer letter is sent.
For smooth client onboarding, multiple calls will be set up to discuss and design all policies.
The Future of EOR Services
As businesses continue to embrace remote work and global expansion, the demand for EOR services is expected to grow. Companies that leverage EORs will gain a competitive edge by accessing top talent, ensuring compliance, and reducing operational complexities. The flexibility and scalability offered by EORs make them an indispensable part of modern business strategies.
Conclusion
In today’s dynamic business landscape, EORs provide the perfect solution for companies seeking to expand globally, optimize operations, and mitigate risks. By taking on the administrative and legal responsibilities of employment, EORs empower businesses to focus on growth and innovation. Whether you are a startup, SME, or large corporation, partnering with an EOR can transform the way you operate, setting you up for long-term success.
FAQs
An EOR is the legal employer, while a PEO shares employment responsibilities with the client company.
EORs typically charge a monthly fee per employee or a percentage of the payroll, depending on the agreement.
The EOR typically provides employees with the same benefits as they would receive in a traditional employment setup, such as health insurance, reimbursement, and paid time off.
International hiring laws differ based on the country, including rules on taxation, employment contracts, and worker classification. It’s important to understand each country’s legal framework before hiring internationally.
Effective communication, time zone management, and building a strong remote work culture are key to managing international teams successfully.