EOR vs Legal Entity
February 23rd, 2023

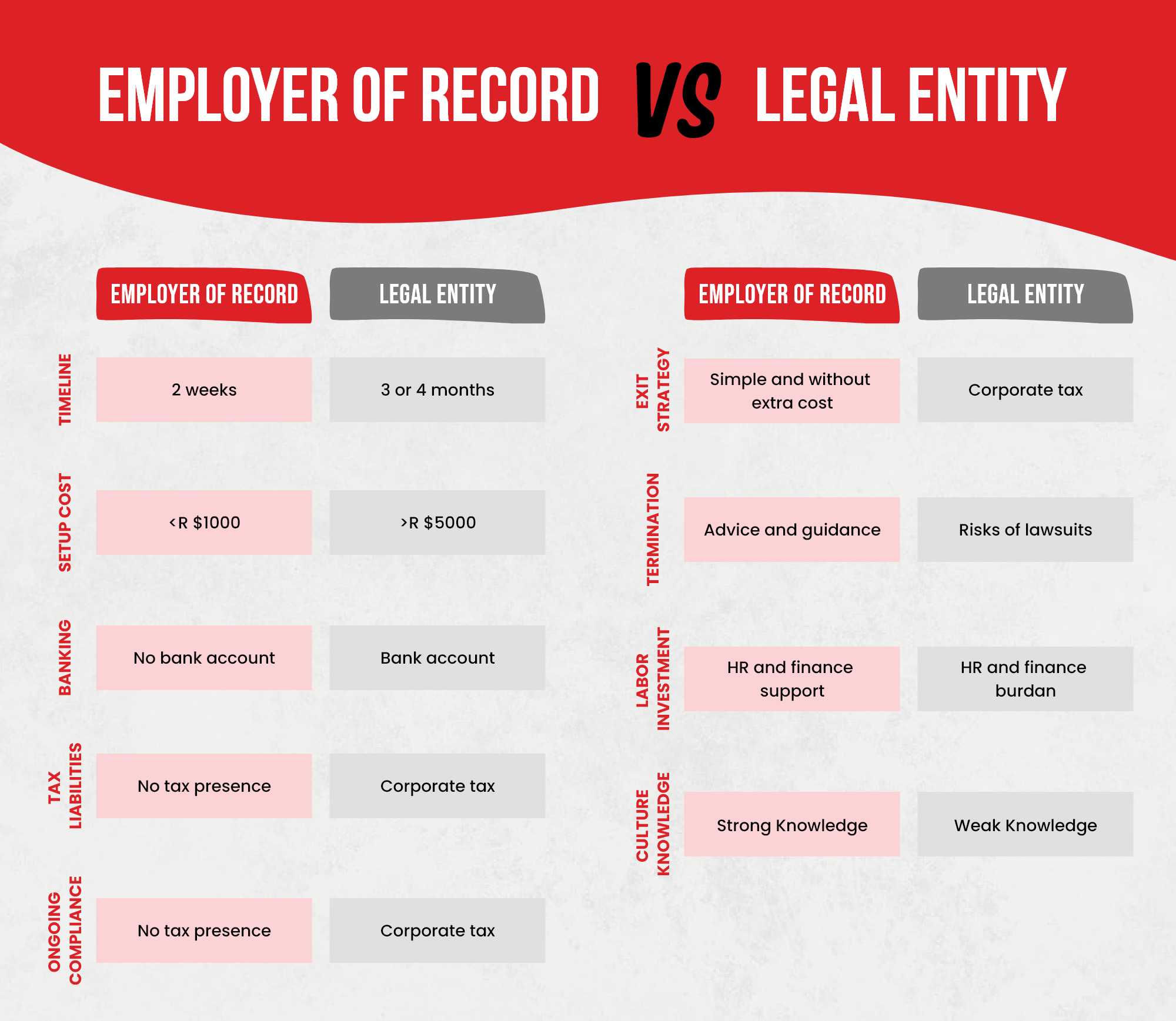
When expanding a business into a new country, there are many considerations to take into account. One important decision to make is whether to set up a legal entity in the new country or use an employer of record (EOR) service. Both options have their benefits and drawbacks, and the choice will depend on the specific circumstances of the business.
Entity Setup
Setting up a legal entity involves registering a new company with the government of the country in which you wish to operate. This can be a lengthy and complicated process, requiring legal and financial expertise. However, once the company is set up, it is fully responsible for its own compliance with local laws and regulations, as well as its own tax liabilities.
One of the primary benefits of setting up a legal entity is that it gives the company full control over its operations in the new country. It can hire its own staff, negotiate contracts with clients and suppliers, and establish its own legal and financial structures. This can be particularly important if the company intends to establish a long-term presence in the new country, as it provides a stable and reliable legal framework.
However, setting up a legal entity can be a complex and costly process. It requires significant time and resources to research local laws and regulations, obtain legal and financial advice, and complete the necessary paperwork. It may also require the hiring of local staff, which can be a significant cost in itself.
Employer of Record
An employer of record (EOR) is a company that provides services to manage the legal and administrative aspects of employment in a foreign country. Essentially, the EOR acts as the legal employer of the staff, handling payroll, tax compliance, and other administrative tasks on behalf of the client company. The client company remains responsible for managing the day-to-day operations of the staff, but the EOR takes care of the legal and financial requirements.
One of the primary benefits of using an EOR is that it can significantly reduce the time and cost involved in setting up a legal entity. The EOR has already established legal and financial structures in the new country, and can handle much of the paperwork and administrative tasks on behalf of the client company. This can be particularly useful for companies that only intend to operate in the new country for a limited period of time, or that want to test the market before committing to a full legal entity.
However, using an EOR can also have drawbacks. The client company may have less control over its operations in the new country, as it is reliant on the EOR to manage the legal and financial aspects of employment. There may also be limitations on the type of staff that can be hired, as the EOR may only be able to provide services for certain types of employment.
Choosing the Right Option
When deciding between entity setup and employer of record, it is important to consider the specific circumstances of the business. Factors such as the length of time the company intends to operate in the new country, the level of control it wants over its operations, and the budget available for expansion will all play a role in the decision.
Ultimately, both options have their benefits and drawbacks, and the choice will depend on the specific needs of the business. By carefully considering the options and seeking expert advice, companies can make an informed decision that will help them to successfully expand their operations into new markets.